What is StilachiRAT Malware?
In November 2024, researchers specializing in incident response uncovered a remote access Trojan (RAT) named StilachiRAT. This finding underscores the dynamic landscape of cyber threats, as the malware integrates multiple harmful functionalities into a single tool for greater effectiveness.
Crafted to avoid detection and extract sensitive information, StilachiRAT captures credentials and retrieves and decrypts usernames and passwords saved in Google Chrome. It conducts thorough system reconnaissance, gathering information like operating system details, BIOS serial numbers, camera availability, and active remote desktop protocol (RDP) sessions.
With a primary goal of stealing cryptocurrencies, StilachiRAT scans for as many as 20 crypto wallet extensions in Chrome, including extensions from Coinbase, Fractal, Phantom, Manta, and Bitget. It keeps track of clipboard activity and running applications, specifically targeting sensitive data such as passwords and private keys.
While the malware has not been tied to a specific threat actor or geographic location, current analysis as of March 2025 indicates that it is not yet widespread. Nevertheless, its sophisticated capabilities pose a notable risk to cybersecurity.
Did you know? In November 2024, a North Korean hacking group reportedly named “Sapphire Sleet” was discovered engaging in cryptocurrency theft and corporate espionage.
How Hackers Deceive Users into Installing StilachiRAT
Cybercriminals utilize various deceptive tactics to lure users into installing malware such as StilachiRAT through multiple channels.
These tactics encompass:
- Phishing emails: Attackers deploy phishing emails to trick recipients into opening malicious attachments or clicking on harmful links, paving the way for RAT malware installation. For example, in November 2024, fraudsters sent phishing emails that targeted self-hosted help desk software, distributing AsyncRat, PureLog Stealer, and XWorm RATs.
- Counterfeit browser extensions: Cybercriminals create fake browser extensions that resemble popular ones. When users install these malicious variants, they unwittingly introduce malware like StilachiRAT into their devices.
- Infected downloads: Users may unknowingly download StilachiRAT by visiting compromised websites or acquiring software from unreliable sources. These installations can be bundled with malicious code that activates during the setup process.
- Exploit kits: Attackers make use of exploit kits to exploit software vulnerabilities, delivering RATs such as StilachiRAT without requiring user interaction. These kits automate the management and deployment of exploits against target machines.
- Brute-force RDP attacks: Cybercriminals systematically guess remote desktop protocol (RDP) credentials to gain unauthorized access, allowing them to install malware remotely.
- Infected USB drives: Attackers circulate infected USB devices that automatically install malware upon connection to a computer.
- Drive-by downloads: Simply visiting compromised or malevolent websites can trigger automatic malware downloads without the user’s awareness.
- Deceptive applications and social media links: Scammers may disguise StilachiRAT as legitimate applications or circulate links through social media, deceiving users into installation.
Did you know? In the cybersecurity landscape, the term “zero-day vulnerability” refers to an unknown security flaw in software or hardware. Since developers are unaware of it, no fix or preventive measures exist to counter it.
How Does StilachiRAT Steal Crypto Wallet Information?
Crafted to circumvent conventional security measures, StilachiRAT operates in multiple layers. Grasping its approach, from initial infection to data theft, is vital for safeguarding your digital assets against this potentially damaging threat.
Targeting Specific Digital Wallets
StilachiRAT directs its focus toward designated cryptocurrency wallet extensions for the Google Chrome browser. It inspects the configurations located in the following registry key to see if any extensions are installed:
\SOFTWARE\Google\Chrome\PreferenceMACs\Default\extensions.settings
StilachiRAT specifically targets the following crypto wallet extensions:
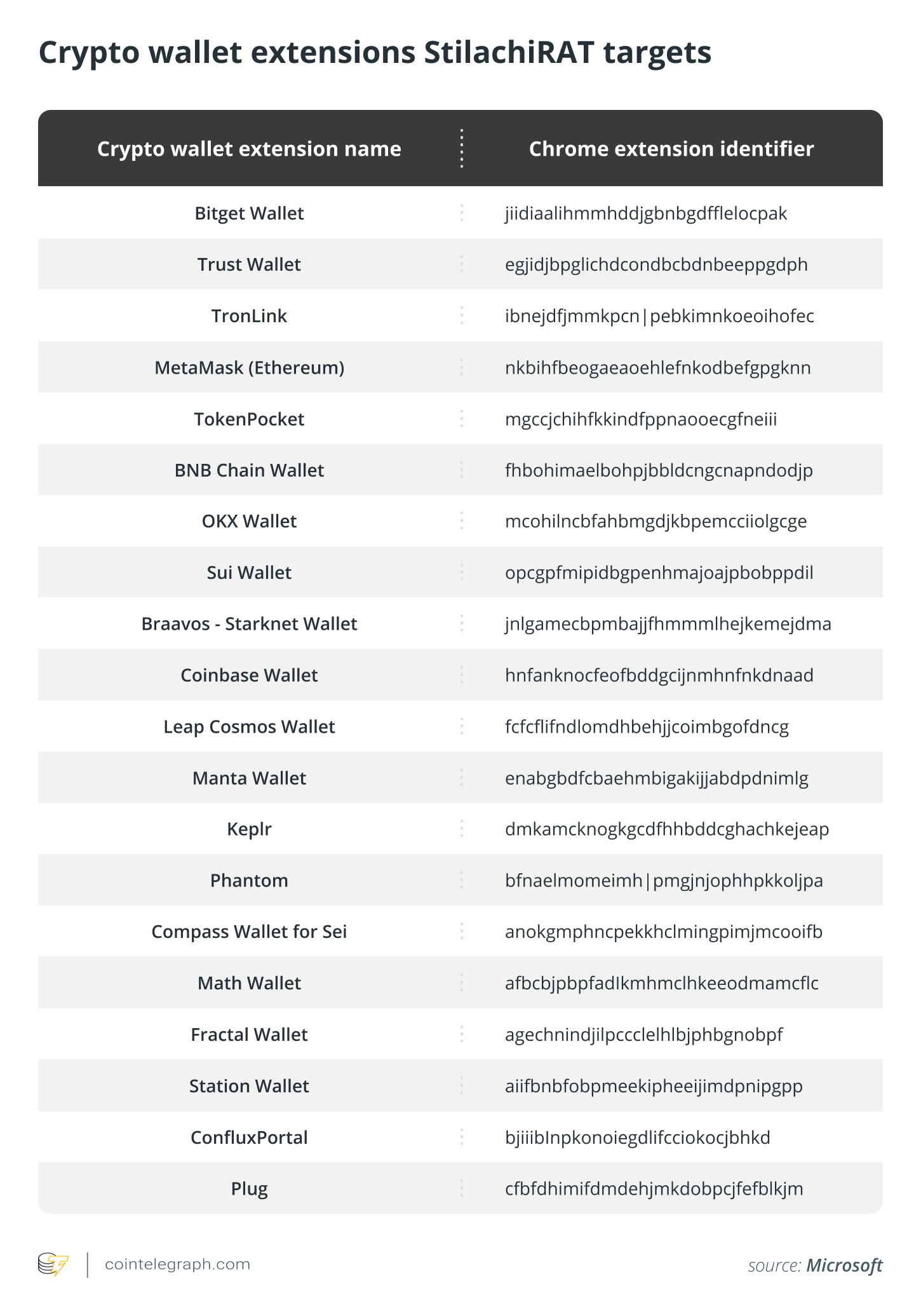
Credential Theft
The malware retrieves Google Chrome’s encryption key from the local state file in the user’s directory. However, as this key is encrypted upon installation, StilachiRAT employs Windows APIs to decrypt it based on the current users’ context, allowing access to credentials stored in Chrome’s password vault. The credentials are extracted from:
- %LOCALAPPDATA%\Google\Chrome\User Data\Local State, which contains Chrome’s configuration data including the encrypted key
- %LOCALAPPDATA%\Google\Chrome\User Data\Default\Login Data, which stores user credentials input into Chrome.
The “Login Data” file is structured as an SQLite database, and StilachiRAT uses a specific database query to extract credentials.

Command-and-Control Operations
Scammers use “command-and-control” servers to execute commands such as system reboots, credential theft, log clearing, application execution, and window manipulation. They can deploy a variety of espionage commands, such as enumerating open windows and modifying registry values.
Each command-and-control server comprises two distinct addresses, one obfuscated and another presented in a binary format. Communication occurs through TCP ports 53, 443, or 16000.
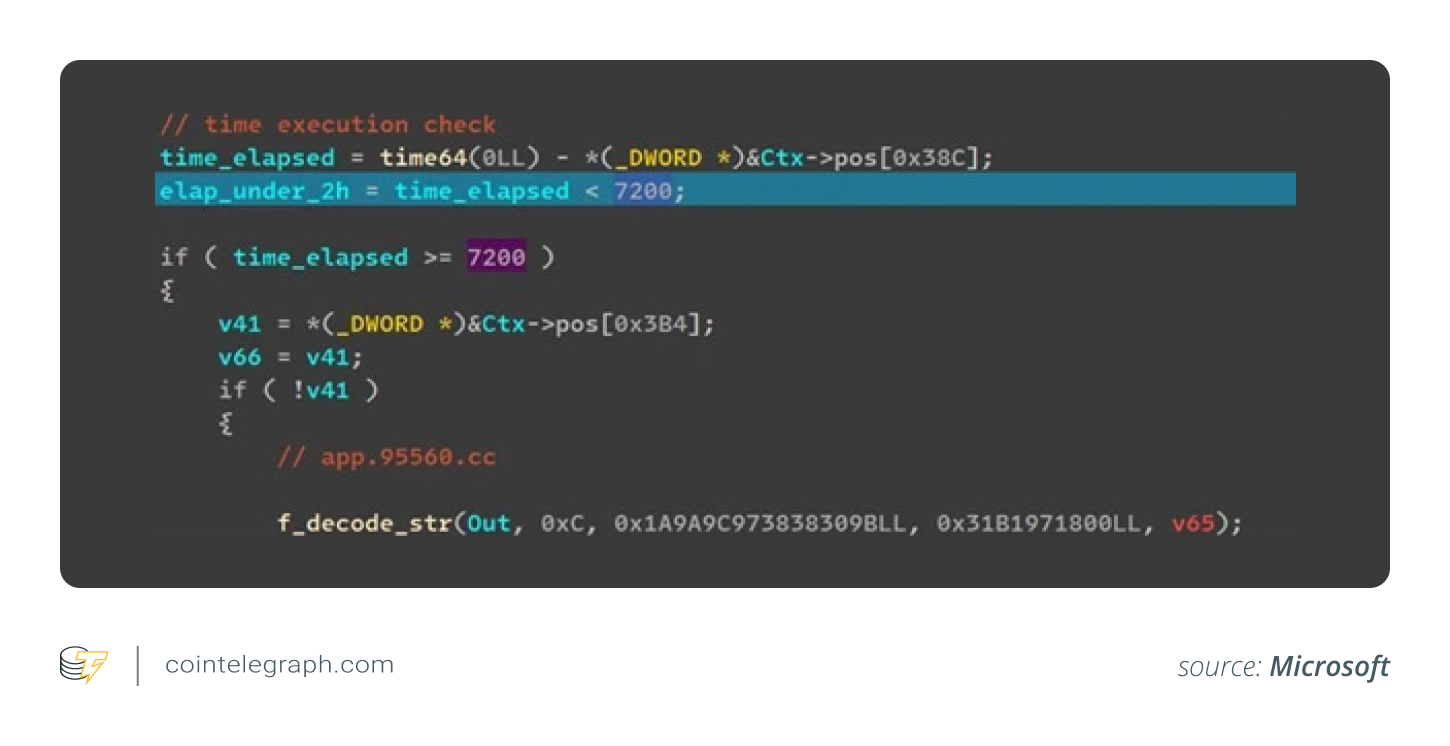
StilachiRAT checks for the presence of “tcpview.exe” and halts operations if detected. To further avoid detection, it delays its initial connection by two hours. Once connected, the malware sends a list of active windows to the server.
Monitoring RDP Sessions
StilachiRAT is capable of monitoring RDP sessions by logging window details and duplicating security tokens to impersonate the user. This poses a severe threat to RDP servers that host administrative sessions.
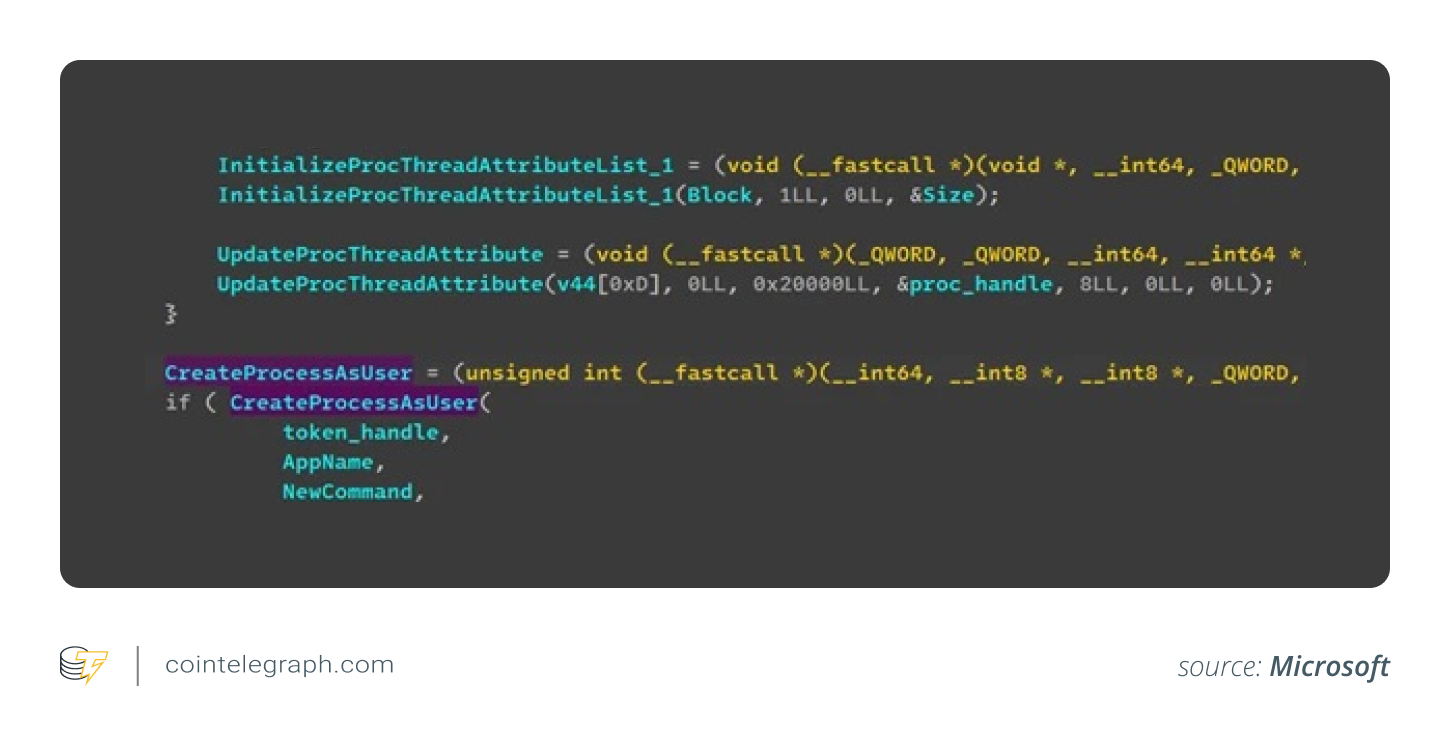
The malware can capture active sessions while dynamically creating foreground windows, thereby enumerating all active RDP sessions. To gain access to each identified session, it retrieves permissions from the Windows Explorer shell and duplicates the security tokens or privileges, enabling the launch of applications using the acquired rights.
Collecting User Data and Monitoring Clipboard Activity
StilachiRAT collects a range of user-related data, including logs of installed software and currently running applications. It tracks active graphical user interface (GUI) windows, their title bar texts, and file paths, transmitting this information back to the command-and-control server, which allows the scammers to monitor user interactions.
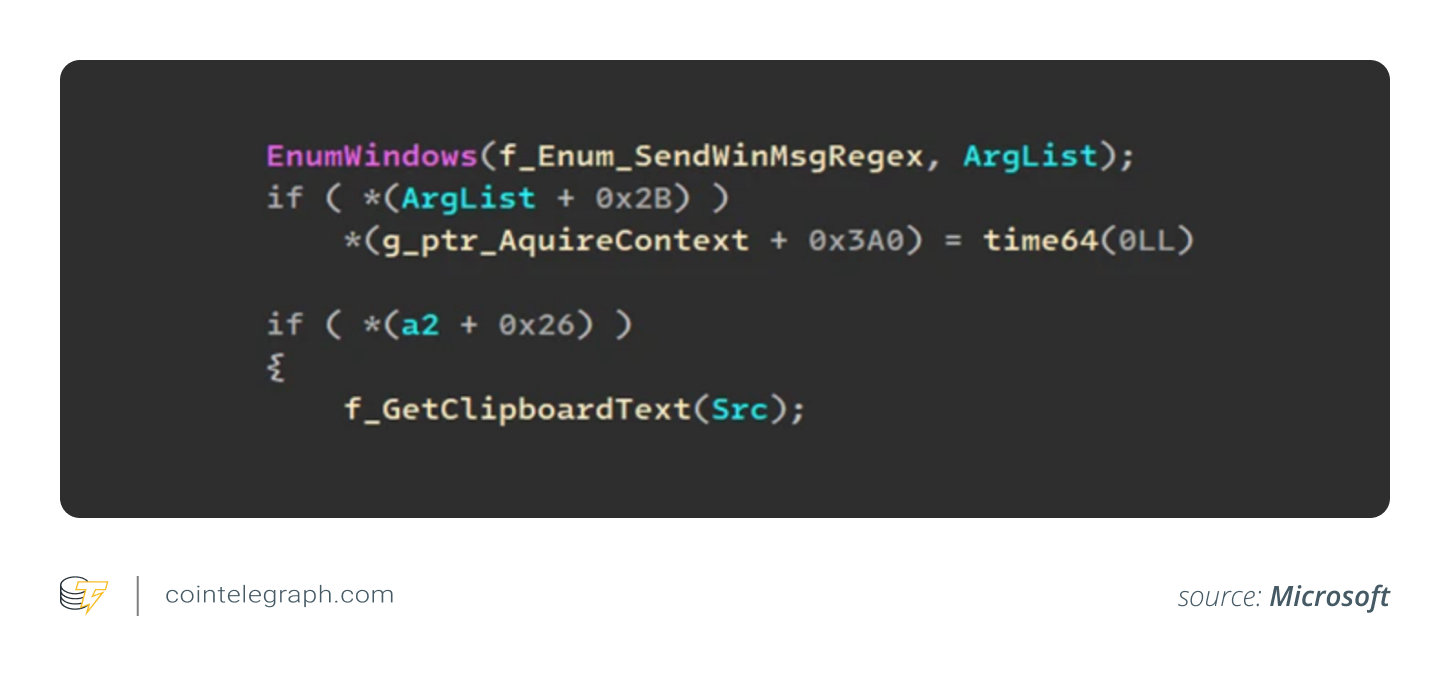
The malware can also monitor clipboard data, reading its content and searching for specific text formats, then forwarding this data to the server. Using this feature, scammers can conduct targeted searches for passwords, cryptocurrency keys, and potentially personal identifiers.
Did you know? Although Google Chrome is available on macOS, its data storage and system integration differ significantly. macOS does not utilize a Windows registry and follows a distinct file system structure and API conventions.
How Does StilachiRAT Evade Detection?
Scammers can run StilachiRAT either as a Windows service or as an independent component. Regardless of the version, there is a mechanism in place to prevent the security system from removing the malware.
The Role of an Observer Thread
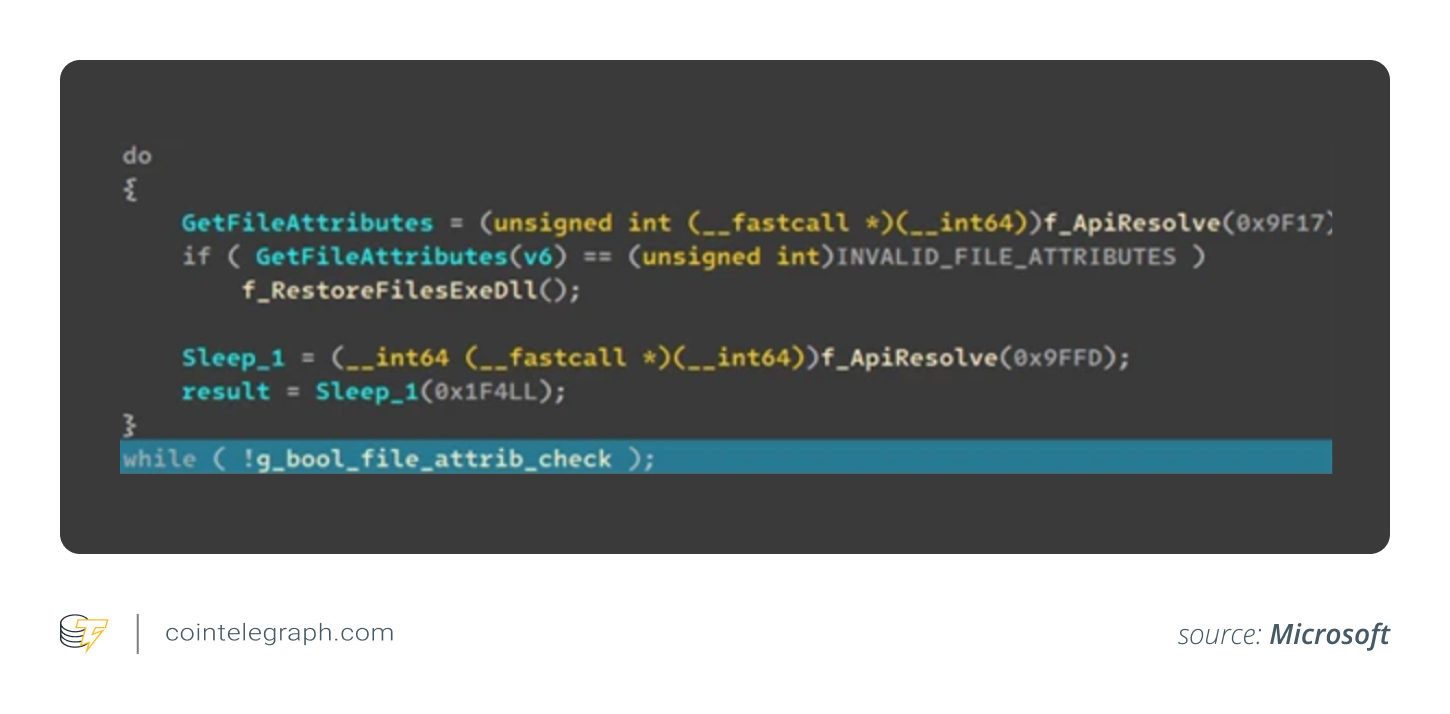
StilachiRAT employs an observer thread that tracks the “EXE” and dynamic link library (DLL) files used by the malware. If at any point these files become unavailable, they are reconstructed from an internal copy obtained during the initialization process. The thread can also recreate the Windows service component by altering the relevant registry settings and restarting it.
Log Removal and Continual Monitoring
To elude detection, StilachiRAT deletes event logs while consistently checking for analysis tools and sandbox timers that may impede its full activation in virtual environments. The malware obfuscates Windows API calls and encodes text strings and values using a custom algorithm, hindering detection by security software.
StilachiRAT employs advanced obfuscation strategies at the API level to complicate manual analysis. Instead of directly referencing Windows APIs, it encodes API names as checksums dynamic at runtime, making it harder to identify during scans.
Additionally, it prevents memory scans from spotting API references by storing precomputed API checksums in various lookup tables, each using a specific XOR value. On execution, StilachiRAT selects the appropriate table according to the hashed API name and applies the necessary XOR mask to decode the value. It also masks cached function pointers with another XOR value, further complicating detection by memory scans.
Strategies for Protecting Against Malware Like StilachiRAT
RATs often masquerade as legitimate software or system updates. To mitigate these risks, it’s essential to download applications exclusively from the official developer’s site or trusted sources. Utilize secure web browsers that can identify and block phishing sites, scams, and malware-hosting pages.
Organizations should implement software that scans and rewrites email URLs to thwart phishing attempts. Employing safe attachments can provide an additional layer of defense by scanning email attachments for potential threats.
It’s crucial to activate network protection to prevent access to malicious websites and online threats. Prior to enabling this feature, it’s wise to audit it in a test environment to identify any applications that may be impacted.
Recommendations include activating safe links and attachments within Office 365 to guard against malicious links and files in phishing attacks, operating endpoint detection and response systems in block mode, enabling protections in Microsoft Defender against potentially unwanted applications (PUAs), and only browsing with systems supporting features to automatically detect and prevent access to harmful websites.
Real-time threat intelligence can limit attack avenues and empower security teams to design detection protocols, modify network surveillance, and shut down malevolent domains or actions before a full-scale compromise occurs. Given StilachiRAT’s evasive capabilities and skill at evading forensic analysis, prompt detection is critical to mitigating any damage.
Did you know? In February 2025, Bybit, a cryptocurrency exchange based in Dubai, suffered a staggering $1.5 billion loss due to a major security breach, which represents the largest recorded crypto theft to date.
Indicators That Your Device is Infected with StilachiRAT
Even though StilachiRAT is designed to be stealthy, there are warning signs that can indicate its presence.
It’s crucial to recognize these indicators and respond before it becomes too late.
- Unusual system behavior: Your device may exhibit slower performance than usual, crash unexpectedly, or frequently freeze.
- Unauthorized access: Suspicious logins to online accounts or unexplained password changes might suggest credential theft.
- Increased network activity: StilachiRAT communicates with remote servers, which could lead to unusual data use or network slowdowns.
- Unexpected pop-ups or programs: You might encounter unfamiliar software, browser extensions, or unrecognized changes in settings.
- Clipboard and browser anomalies: If you notice copied texts or cryptocurrency wallet addresses changing, it likely indicates that the malware is tampering with clipboard data.
How to Eliminate StilachiRAT Malware from Your Device
Having StilachiRAT on your device poses a direct threat to your cryptocurrency holdings. To remove StilachiRAT effectively, adhere to the following steps:
- Disconnect from the internet: This will prevent the malware from communicating with remote servers, sending out data, or receiving instructions.
- Conduct a complete security scan: Utilize a reliable antivirus or anti-malware tool to eliminate StilachiRAT. For added assurance, consider using multiple tools.
- Uninstall suspicious applications: Remove any questionable or unknown software from your system settings.
- Remove harmful browser extensions: Check your browser for unfamiliar extensions, particularly in Google Chrome, and delete any that seem suspicious.
- Reset system settings: Revert browser settings to eliminate any remaining threats, generally found in your device’s settings menu.
- Apply software updates and security patches: Keeping your operating system and applications up to date will aid in preventing reinfection.
- Enable real-time network protection: Activate an anti-malware solution that provides network protection for future safety.
Best Practices for Securing Cryptocurrency Wallets on Chrome
Safeguarding your cryptocurrency assets on Chrome involves proactive measures. Here is a comprehensive guide on fortifying your crypto wallets on the platform.
Select a Secure Wallet Extension
Extensions such as MetaMask and Trust Wallet are recognized for their robust security features and widespread adoption. However, ensure you download extensions directly from the official Chrome Web Store and avoid dubious platforms potentially established by scammers. Before installing any extension, conduct thorough research on the developer, read user reviews, and assess any potential security concerns.
Implement Strong Security Practices
To protect yourself from malware, it’s critical to establish strong security protocols:
- Unique passwords: Use complex and unique passwords for your wallet and Chrome account, and refrain from reusing passwords across different platforms.
- Enable two-factor authentication (2FA): Activate 2FA for your wallet and Chrome account for an added layer of security.
- Keep wallet extensions updated: Ensure that both your Chrome browser and wallet extensions are running the latest versions to patch any security vulnerabilities.
- Secure your device: Protect your device with reliable anti-malware software and firewalls.
- Check for phishing: Utilize tools like Wallet Highlighter to check for suspicious wallet addresses on webpages. Avoid clicking on dubious links or downloading software from untrusted sources.
Key Considerations for Wallet Management Security
Adhering to best practices for managing wallets can help secure your crypto assets:
- Backup your seed phrase: If your wallet uses a seed phrase (or recovery phrase), document it on paper and store it in a secure location.
- Use a password manager: Employ a password manager to safely store and manage your wallet passwords.
- Regularly review transactions: Periodically monitor your wallet activities and check for any unauthorized transactions.
- Exercise caution with DApps: Interact with only trusted and reputable decentralized applications (DApps).
Securing your cryptocurrency wallet in Chrome necessitates a multi-layered strategy. By consistently implementing strong password practices, enabling 2FA, carefully evaluating browser extensions, and keeping your software current, you can significantly reduce the risks associated with online wallet usage. Staying informed about emerging cyber threats and diligently adhering to best practices can help protect your digital assets.
